The Malinowy Zdrój Medical Spa Hotel is located in the Solec - Zdrój Spa Municipality in Świętokrzyskie province. This Świętokrzyski health resort is the only one in the region that has the strongest sulfide brine in the world.
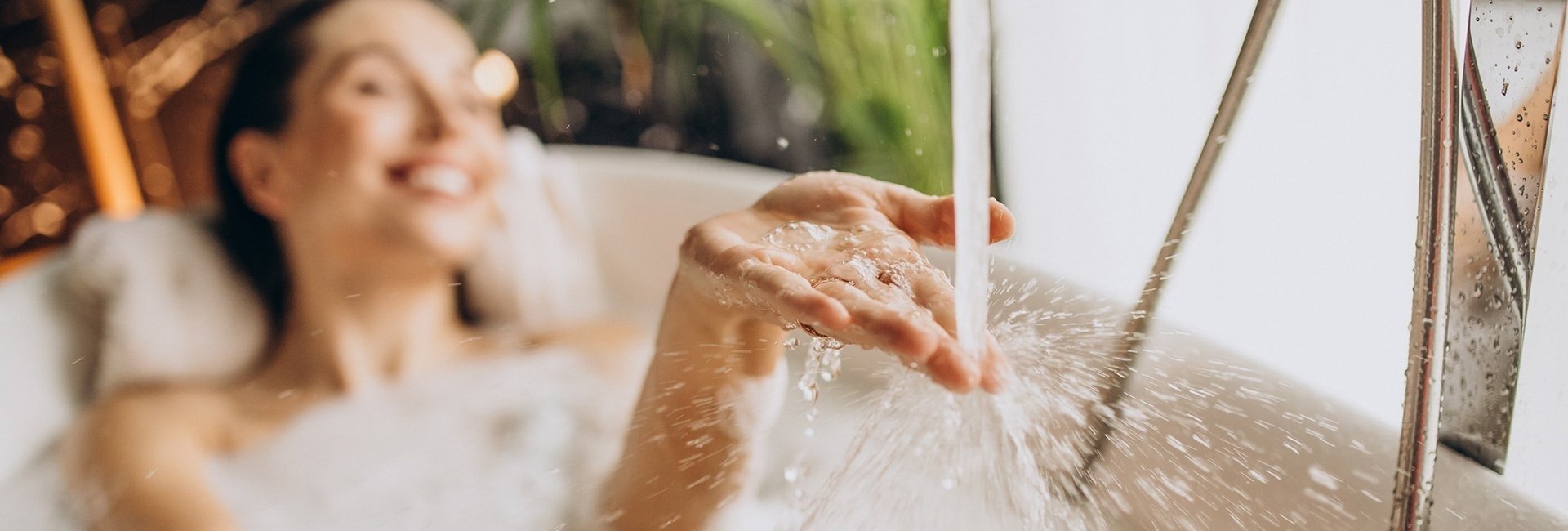

The world's strongest sulfide brine, which we use in Malinowe Hotels Rehabilitation Centers, comes from the ‘Malina’ borehole in the Solec-Zdrój municipality. Its high mineralization and exceptional properties ensure the effectiveness of prevention and treatment. The bath's clear, light colour testifies to the proper preparation of sulfide water, from which no undesirable substances have precipitated. According to specialists, the dark colour of the bath, confirms the process of oxidation of valuable sulfur compounds, which reduces the therapeutic value of the treatment.

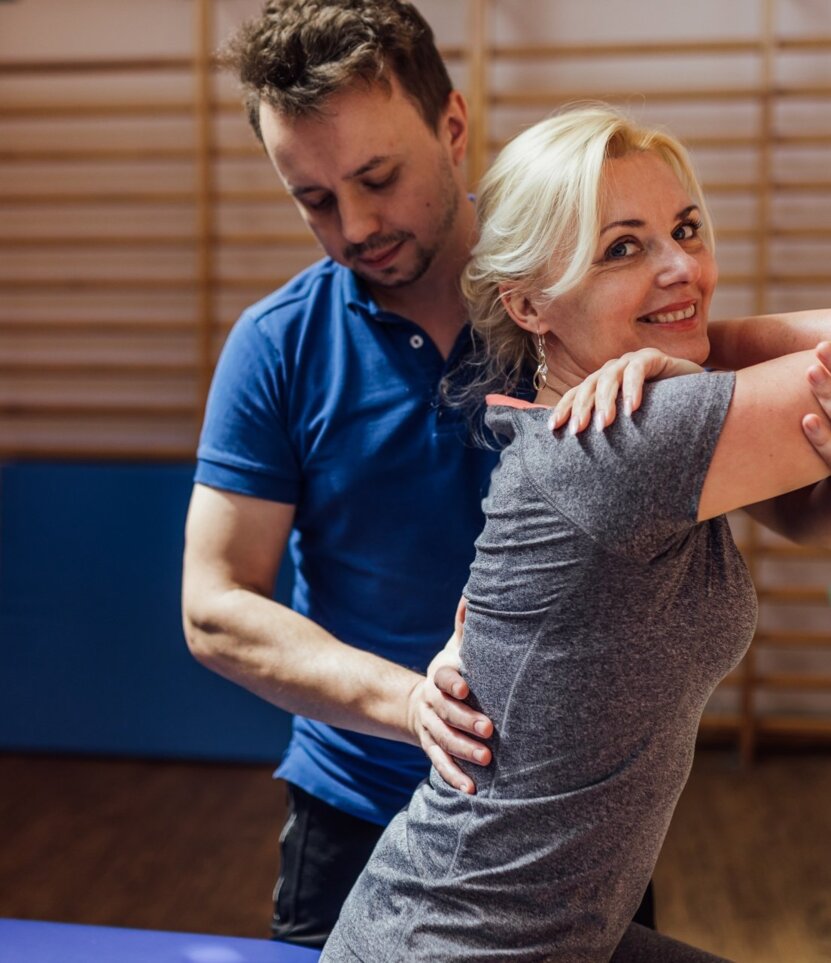
The method of diagnosis and therapy according to the Ackermann concept is currently one of the most effective and complementary methods of manual treatment. It is distinguished by rapid and targeted diagnosis and the therapeutic procedure here is precise and accurate.
